There is no reasoning, no process of inference or comparison; there is no thinking about things, no putting two and two together; there are no ideas — the animal does not think of the box or of the food or of the act he is to perform. — Edward Thorndike(1874–1949), the psychologist who proposed Law of effect.
While Convolution Neural Network (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) are becoming more important for businesses due to their applications in Computer Vision (CV) and Natural Language Processing (NLP), Reinforcement Learning (RL) as a framework for computational neuroscience to model decision making process seems to be undervalued. Besides, there seems to be very little resources detailing how RL is applied in different industries. Despite the criticisms about RL’s weaknesses, RL should never be neglected in the space of corporate research given its huge potentials in assisting decision making. As Koray Kavukcuoglu, the director of research at Deepmind, said at a conference,
“If one of the goals that we work for here is AI then it is at the core of that. Reinforcement Learning is a very general framework for learning sequential decision making tasks. And Deep Learning, on the other hand, is of course the best set of algorithms we have to learn representations. And combinations of these two different models is the best answer so far we have in terms of learning very good state representations of very challenging tasks that are not just for solving toy domains but actually to solve challenging real world problems.”
Therefore, this article aims to 1)investigate the breadth and depth of RL applications in real world; 2)view RL from different aspects; and 3)persuade the decision makers and researchers to put more efforts on RL research.
The rest of the article is organized as follows. Section I is a general introduction. Section II presents the applications of RL in different domains and a brief description of how it was applied. Section III summarizes the things one would need to apply RL. Section IV is the intuition from other disciplines and Section V is about how RL could be useful in the future. Section VI is conclusion.
I. Introduction to Reinforcement Learning
RL, known as a semi-supervised learning model in machine learning, is a technique to allow an agent to take actions and interact with an environment so as to maximize the total rewards. RL is usually modeled as a Markov Decision Process (MDP).
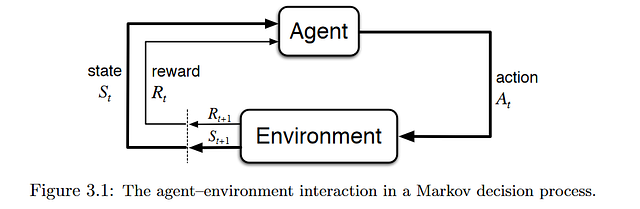
Source: Reinforcement Learning:An Introduction
Imagine a baby is given a TV remote control at your home (environment). In simple terms, the baby (agent) will first observe and construct his/her own representation of the environment (state). Then the curious baby will take certain actions like hitting the remote control (action) and observe how would the TV response (next state). As a non-responding TV is dull, the baby dislike it (receiving a negative reward) and will take less actions that will lead to such a result(updating the policy) and vice versa. The baby will repeat the process until he/she finds a policy (what to do under different circumstances) that he/she is happy with (maximizing the total (discounted) rewards).
The study of RL is to construct a mathematical framework to solve the problems. For example, to find a good policy we could use valued-based methods like Q-learning to measure how good an action is in a particular state or policy-based methods to directly find out what actions to take under different states without knowing how good the actions are.
However, the problems we face in the real world can be extremely complicated in many different ways and therefore a typical RL algorithm has no clue to solve. For example, the state space is very large in the game of GO, environment cannot be fully observed in Poker game and there are lots of agents interact with each other in the real world. Researchers have invented methods to solve some of the problems by using deep neural network to model the desired policies, value functions or even the transition models, which therefore is called Deep Reinforcement Learning. This article makes no distinction between RL and Deep RL.
There are lots of good stuffs about RL online and interested readers can visit awesome-rl, argmin and dennybritz.
II. Applications
This part is written for general readers. At the same time, it will be of greater value for readers with some knowledge about RL.
Resources management in computer clusters
Designing algorithms to allocate limited resources to different tasks is challenging and requires human-generated heuristics. The paper “Resource Management with Deep Reinforcement Learning” [2] showed how to use RL to automatically learn to allocate and schedule computer resources to waiting jobs, with the objective to minimize the average job slowdown.
State space was formulated as the current resources allocation and the resources profile of jobs. For action space, they used a trick to allow the agent to choose more than one action at each time step. Reward was the sum of (-1/duration of the job) over all the jobs in the system. Then they combined REINFORCE algorithm and baseline value to calculate the policy gradients and find the best policy parameters that give the probability distribution of actions to minimize the objective. Click here to view the code on Github.
Traffic Light Control
In the paper “Reinforcement learning-based multi-agent system for network traffic signal control”[3], researchers tried to design a traffic light controller to solve the congestion problem. Tested only on simulated environment though, their methods showed superior results than traditional methods and shed a light on the potential uses of multi-agent RL in designing traffic system.
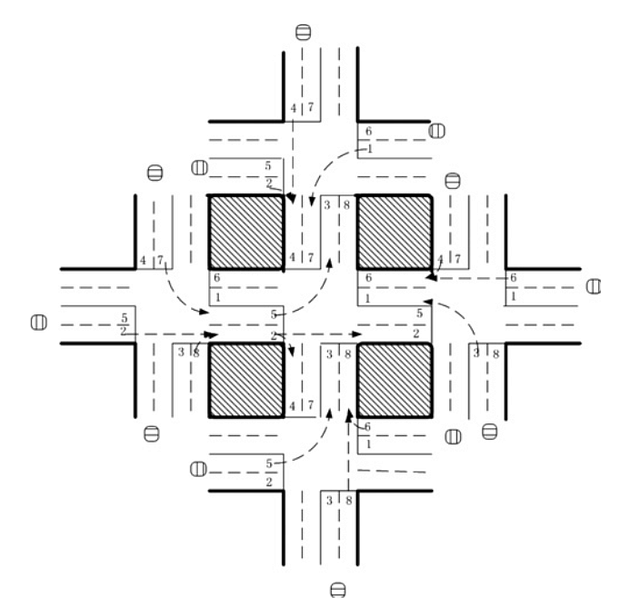
Five-intersection traffic network. Source.
Five agents were put in the five-intersection traffic network, with a RL agent at the central intersection to control traffic signaling. The state was defined as eight-dimensional vector with each element representing the relative traffic flow of each lane. Eight choices were available to the agent, each representing a phase combination, and the reward function was defined as reduction in delay compared with previous time step. The authors used DQN to learn the Q value of the {state, action} pairs.
Robotics
There are tremendous work on applying RL in Robotics. Readers are referred to [10] for a survey of RL in Robotics. In particular, [11] trained a robot to learn policies to map raw video images to robot’s actions. The RGB images were fed to a CNN and outputs were the motor torques. The RL component was the guided policy search to generate training data that came from its own state distribution.
Web System Configuration
There are more than 100 configurable parameters in a web system and the process of tuning the parameters requires a skilled operator and numerous trail-and-error tests. The paper “A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Online Web System Auto-configuration” [5] showed the first attempt in the domain on how to do autonomic reconfiguration of parameters in multi-tier web systems in VM-based dynamic environments.
The reconfiguration process can be formulated as a finite MDP. The state space was the system configuration, action space was {increase, decrease, keep} for each parameter, and reward was defined as the difference between the given targeted response time and measured response time. The authors used the model-free Q-learning algorithm to do the task.
Although the authors used some other technique like policy initialization to remedy the large state space and computational complexity of the problem instead of the potential combinations of RL and neural network, it is believed that the pioneering work has paved the way for future research in this area.
Chemistry
RL can also be applied in optimizing chemical reactions.[4] showed that their model outperformed a state-of-the-art algorithm and generalized to dissimilar underlying mechanisms in the paper “Optimizing Chemical Reactions with Deep Reinforcement Learning”.
Combined with LSTM to model the policy function, the RL agent optimized the chemical reaction with the Markov decision process (MDP) characterized by {S, A, P, R}, where S was the set of experimental conditions (like temperature, pH, etc), A was the set all possible actions that can change the experimental conditions, P was the transition probability from current experiment condition to the next condition, and R was the reward which is a function of the state.
The application is a great one to demonstrate how RL can reduce time-consuming and trial-and-error work in a relatively stable environment.
Personalized Recommendations
Previous work of news recommendations faced several challenges including the rapid changing dynamic of news, users get bored easily and Click Through Rate cannot reflect the retention rate of users. Guanjie et al. have applied RL in news recommendation system in a paper titled “DRN: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for News Recommendation” to combat the problems [1].
In practice, they constructed four categories of features, namely A)user features and B)context features as the state features of the environment, and C)user-news features and D)news features as the action features. The four features were input to the Deep Q-Network(DQN) to calculate the Q-value. A list of news were chosen to recommend based on the Q-value, and the user’s click on the news was a part of the reward the RL agent received.
The authors also employed other techniques to address other challenging problems, including memory replay, survival models, Dueling Bandit Gradient Descent and so on. Please refer to the paper for details.
Bidding and Advertising
Researchers from Alibaba Group published a paper “Real-Time Bidding with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learningin Display Advertising” [6] and claimed that their distributed cluster-based multi-agentbidding solution (DCMAB) has achieved promising results and thus they plan to conduct a live test in Taobao platform.
The details of the implementation are left to users to investigate. Generally speaking, Taobao ad platform is a place for merchants to place a bid in order to display ad to the customers. This could be a multi-agent problem because the merchants are bidding against each other and their actions are interrelated. In the paper, merchants and customers were clustered into different groups to reduce computational complexity. The state space of the agents indicated the cost-revenue status of the agents, action space was the bid (continuous), and reward was the revenue caused by the customer cluster.

The DCMAB algorithm. Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1802.09756.pdf
Other questions, including the impact of different reward settings (self-interested vs coordinate) on agents’ revenue were also studied in the paper.
Games
RL is so well-known these days because it is the mainstream algorithm used to solve different games and sometimes achieve super-human performance.
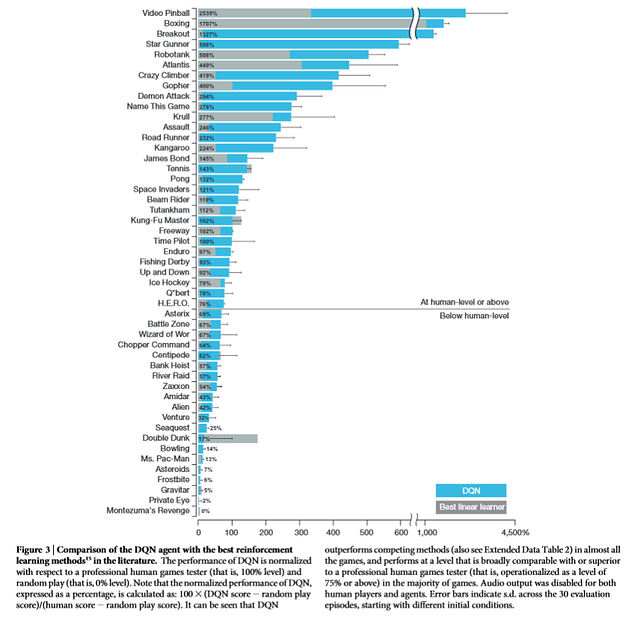
RL vs linear model vs Human. Click here for the source.
The most famous one must be AlphaGo[12] and AlphaGo Zero[13]. AlphaGo, trained with countless human games, already achieved super-human performance by using value network and Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) in its policy network. Yet, the researchers later on thought back and tried a purer RL approach — train it from scratch. The researchers let the new agent, AlphaGo Zero, played with itself and finally beat AlphaGo 100–0.
Deep Learning
More and more attempts to combine RL and other deep learning architecture can be seen recently and they showed impressive results.
One of the most influential work in RL is the pioneering work of Deepmind to combine CNN with RL [7]. By doing so, the agent has the ability to “see” the environment through high-dimensional sensory and then learn to interact with it.
RL and RNN is another combinations people used to try new idea. RNN is a type of neural network that has “memories”. When combined with RL, RNN gives the agents’ ability to memorize things. For example, [8] combined LSTM with RL to create Deep Recurrent Q-Network(DRQN) to play Atari 2600 games. [4] also used RNN and RL to solve chemical reaction optimization problem.
Deepmind showed [9] how to use generative models and RL to generate programs. In the model, the adversarially trained agent used the signal as rewards to improve the actions, instead of propagating the gradients to the input space as in the GAN training

Input vs Generated result. See source.
III. What you need to know before applying RL to your problem
There are several things needed before RL can be applied:
- Understanding your problem: You do not necessarily need to use RL in your problem and sometimes you just cannot use RL. You may want to check if your problem has some of the following characteristics before deciding to use RL: a) trial-and-error (can be learned to do better by receiving feedback from the environment); b)delayed rewards; c)can be modeled as MDP; d)your problem is a control problem.
- A simulated environment: Lots of iterations are needed before a RL algorithm to work. I am sure that you don’t want to see a RL agent trying different things in a self-driving car on a highway, right? Therefore, a simulated environment that can correctly reflect the real world is needed.
- MDP: You world need to formulate your problem into a MDP. You need to design the state space, action space, reward function and so on. Your agent will do what it is rewarded to do under the constraints. You may not get the results you want if you design the things differently.
- Algorithms: There are different RL algorithms you can choose and questions to ask yourself. You want to directly find out the policy or you want to learn the value function? You want to go model-free or model-based? Do you need to combine other kinds of deep neural network or methods to solve your problems?
To stay objective and fair, you are also warned about the shortcomings of RL and here is a great post about it.
IV. Intuitions from other disciplines
RL has a very close relationship with psychology, biology and neuroscience. If you think about it, what a RL agent does is just trial-and-error: it learns how good or bad its actions are based on the rewards it receives from the environment. And this is exactly how human learns to make a decision. Besides, the exploration and exploitation problem, credit assignment problem, attempts to model the environment are also something we face in our everyday life.
The Economics theory can also shed some light on RL. In particular, the analysis of multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) can be understood from the perspectives of game theory, which is a research area developed by John Nash to understand the interactions of agents in a system. In addition to game theory, MARL, Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) could also be useful to understand other economic topics like market structure (e.g.monopoly, oligopoly, etc), externality and information asymmetry.
V. What could RL possibly achieve in the future
RL still has lots of problems and cannot be used easily. Yet, as long as more efforts are put in solving the problems, RL would be influential and impactful in the following ways:
- Assisting human: Maybe it is too much to say RL can one day evolve into artificial general intelligence (AGI), but RL surely has the potential to assist and work with human. Just imagine a robot or a virtual assistant working with you and taking your actions into its considerations to take actions in order to achieve a common goal. Wouldn’t it be great?
- Understanding the consequences of different strategies: Life is so amazing because time will not go back and things just happen once. Yet, sometimes we would like to know how things could be different (at least in the short term) if I took a different action? Or would Croatia has a greater chance to win the 2018 World Cup if the coach used another strategy? Of course, to achieve this we would need to model the environment, transition functions and so on perfectly and also analyse the interactions between the agents, which seems to be impossible at the moment.
VI. Conclusion
This article just showed some of the examples of RL applications in various industries. They should not limit your RL use case and as always, you should use first principle to understand the nature of RL and your problem.
If you are a decision maker of a company, I hope this article is enough to persuade you to rethink about your business and see if RL can be potentially used. If you are a researcher, I hope you would agree with me that although RL still has different shortcomings, it also means it has lots of potentials to improve and lots of research opportunities.
What are your thoughts? Can you think of any problem that RL could solve?
References
[1]G. Zheng, F. Zhang, Z. Zheng, Y. Xiang, Ni. J. Yuan, X. Xie, and Z. Li. DRN: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Frameworkfor News Recommendation. 2018.
[2] H.Mao, Alizadeh, M. Alizadeh, Menache, I.Menache, and S.Kandula. Resource Management With deep Reinforcement Learning. In ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks, 2016.
[3] I. Arel, C. Liu, T. Urbanik, and A. Kohls, “Reinforcement learning-basedmulti-agent system for network traffic signal control,”IET IntelligentTransport Systems, 2010.
[4] Z. Zhou, X. Li, and R. N. Zare. Optimizing Chemical Reactions with Deep Reinforcement Learning. ACSCentral Science3, 2017.
[5] X. Bu, J. Rao, C. Z. Xu. A reinforcement learning approach to online web systems auto-configuration. In Distributed Computing Systems, 2009. ICDCS’09.29th IEEE International Conference on. IEEE , 2019.
[6]J. Jin, C.Song, H. Li, K. Gai, J.Wang amd W. Zhang. Real-Time Bidding with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learningin Display Advertising. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.09756, 2018.
[7] V. Mnih, K. Kavukcuoglu, D. Silver, A. Graves, I. Antonoglou, D. Wierstra, and M. Riedmiller. Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.5602, 2013.
[8] M. J. Hausknecht and P. Stone. Deep Recurrent Q-Learning For Partially Observable MDPs. Proc. of Conf. on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI, 2015.
[9] Y. Ganin, T. Kulkarni, I. Babuschkin, S. Eslami and O. Vinyals. Synthesizing Programs For Images Using Reinforced Adversarial Learning. arXiv preprintarXiv:1804.01118.
[10] J. Kober, J. A. D. Bagnell, J. Peters. Reinforcement Learning in Robotics: A survey. Int. J. Robot. Res. Jul. 2013.
[11] S. Levine, C. Finn, T. Darrell, and P. Abbeel. End-to-end Training of Deep Visuomotor Policies. arXiv preprint arXiv:1504.00702, 2015.
[12] D. Silver, A. Huang, A., C.J. Maddison, A. Guez, L. Sifre,G. van den Driessche, J. Schrittwieser, I. Antonoglou, V. Panneershelvam, M. Lanctot, S. Dieleman, D. Grewe, J. Nham, N. Kalchbrenner, I. Sutskever, T. Lillicrap, M. Leach, K. Kavukcuoglu, T. Graepel, and D. Has-sabis. Mastering the game of go with deep neuralnetworks and tree search.Nature, 529(7587). 2016.
[13] D. Silver, J. Schrittwieser, K. Simonyan, I. Antonoglou, A. Huang, A. Guez, T. Hubert, L. Baker, M. Lai, A. Bolton, Y. Chen,T. Lillicrap, F. Hui, L. Sifre, G. van den Driessche, T. Graepel, and D. Hassabis. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge.Nature, 2017.