Ready to learn Artificial Intelligence? Browse courses like Uncertain Knowledge and Reasoning in Artificial Intelligence developed by industry thought leaders and Experfy in Harvard Innovation Lab.
Due to its deep learning and independent decision-making capabilities, applications of AI in different business areas are seeing a steady rise in ubiquity in some industries.
The concept of artificial intelligence or machines that aim to emulate human thinking is undergoing vigorous research and is a topic that is increasingly being associated with the Internet of things. An AI enabled IoT system extends the functionality and value of an organization’s offering, without the need for committing additional resources to achieve the increased value. This is exemplified by under Armour(UA) and IBM’s collaboration on the UA Record app, which is an AI-based personal fitness coaching system, that uses a variety of sensor data to suggest highly personalized, context-relevant fitness activities to users. Such applications of AI are going to be more commonplace in the future as they are already having a significant impact on many industries. Here are a few application areas that you can consider for AI implementation:
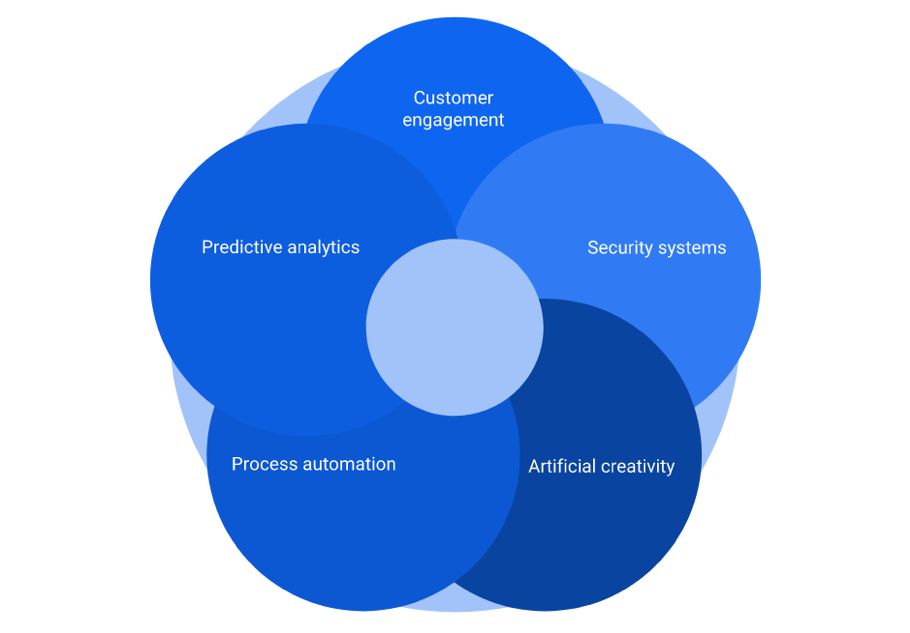
APPLICATIONS OF AI IN DIFFERENT BUSINESS AREAS
Customer engagement
As businesses, especially in the service sector industries, evolve from the basic transactional model of customer interaction to a more continuous engagement sequence, the role of IoT and artificial intelligence is rapidly gaining importance. For example, the use of digital concierge and virtual assistants is being discussed in the hospitality industry to automate, personalize and streamline interactions between guests and the service delivery system. The trial deployment of an AI assistant at the Munich airport that helps visitors with directions is an example that forebodes the use of AI in similar cases and for broader purposes in the future. Improved engagement can also be extended to employees by using virtual employee assistants to ensure continued connectivity and simplified task execution.
Predictive analytics
Growing applications of IoT in enterprises has entailed a corresponding increase in the data being generated by the installed systems. This data, continuously collected through the myriad of sensors used in the system, can be used in machine learning models that can be used to make highly informed decisions. The enormity of data volume can be easily managed using AI based data management tools and then be used to derive insights that impact more than just the operational performance. For example, in a healthcare institution, continuous diagnostic analysis is performed to track operational parameters such as the availability of personnel, machines, drugs and other resources; the utilization of different functional units; and the number and types of cases being admitted; to improve responsiveness to changing conditions. AI can be used to perform predictive analysis to ensure preparedness of the facility to respond to different situations and can also be used to provide prescriptive long-term solutions to repetitive issues.
Security systems
IoT sensors that scan biometric information to authenticate the identity are already being used by numerous business and government organizations. Combining IoT and AI can make biometric scanning even more effective and secure by including the recognition of facial features and voice. CCTV cameras used today require a pair of human eyes to monitor the live footage and identify potential threats or to find clues after an incident. AI infused security camera networks enable scanning of multiple parameters including movements and high risk objects, and automatically raise alarm when a potentially suspicious event occurs. Use of AI surveillance systems like Ella, which finds and distinguishes video footage elements for easy identification of suspicious or missing items, is one way AI can be used for enhanced security.
Process automation
Manufacturing automation has been one of the earliest areas of application of robotics and artificial intelligence. A manufacturing process operated by an AI control system, that is linked to sources of different kinds of data, from the demand in market to the availability of parts from vendors; can function with maximum efficiency, as the process can be regulated through real-time analysis of data. Even service organizations such as restaurants can automate processes by using automated kitchen robots for cooking that emulates human chefs.
Artificial creativity
Artificial creativity is the concept of using algorithms that allow machines to produce content that is random yet desirable for human perception. Multiple online services that provide AI compositions to inspire or completely create new content are already available, and are indicative of a future where an increasing portion of creative content will be inspired or created by AI technology. The focus of AI implementation at present must be to minimize human involvement in the routine and non-creative tasks, so that human effort can be directed towards innovation and planning, where AI can be used for guidance. Following the lead of industry leaders, organizations aiming for sustained relevance should prepare for the use of AI based technology, embedded in an IoT foundation.