2019 vulnerabilities statistics
Vulnerabilities by OWASP category
Most common vulnerability – injection
Increase in the number of vulnerabilities in third-party components
DoS and CSRF
An unexpected decrease in IoT vulnerabilities
API vulnerabilities – growing, but slowing
Content management systems
Server technologies
Databases
Social media analysis
| CVE ID | DESCRIPTION | CVSS SCORE | DATE PUBLISHED |
| CVE-2019-0708 | Microsoft Windows Remote Desktop Services RDP Connection Request Handling Remote Code Execution | 10 | 16/05/2019 |
| CVE-2019-14287 | Sudo Runas Specification ALL Keyword Local Command Execution | 8.8 | 14/10/2019 |
| CVE-2019-11932 | WhatsApp Messenger for Android GIF Image Handling Function Arbitrary Code Execution | 8.8 | 02/10/2019 |
| CVE-2019-1040 | Microsoft Windows MitM NTLM MIC Protection Bypass | 5.9 | 12/06/2019 |
| CVE-2019-11043 | Remote Code Execution Vulnerability In PHP-FPM (The Fastcgi Process Manager) Running On The Nginx Server | 9.8 | 28/10/2019 |
| CVE-2019-11931 | WhatsApp MP4 File Elementary Stream Metadata Handling Remote Stack Buffer Overflow | 7.8 | 14/11/2019 |
| CVE-2019-2215 | Linux Kernel Binder (The Main Inter-Process Communication System In Android) Use-after-free Local Privilege Escalation | 7.8 | 11/10/2019 |
| CVE-2019-8777 | Apple macOS FaceTime Lock Screen Handling Unspecified Local Contact Information Disclosure | 1.2 | 10/10/2019 |
| CVE-2019-11510 | Pulse Connect Secure Web Service HTML5 Access Feature Path Traversal Remote File Disclosure | 10 | 26/04/2019 |
| CVE-2019-2107 | Google Android Media Framework Unspecified File Handling Arbitrary Code Execution | 8.8 | 01/07/2019 |
The interesting conclusion we drew from the analysis of these tweets was that the CVSS score that most of the industry relies on to prioritize systems patching doesn’t necessarily correlate with the vulnerability popularity (at least in social media). While 95% of vulnerabilities are mentioned in fewer than 40 tweets, there are some “superstars” that feature in thousands of posts and reposts. In Figure 12 you can see the distribution of vulnerabilities by CVSS score and their virality in social media. While it’s not hard to notice a trend for more viral vulnerabilities among high CVSS scores, there are dozens of vulnerabilities in the Medium severity range that also reached high popularity in social media.
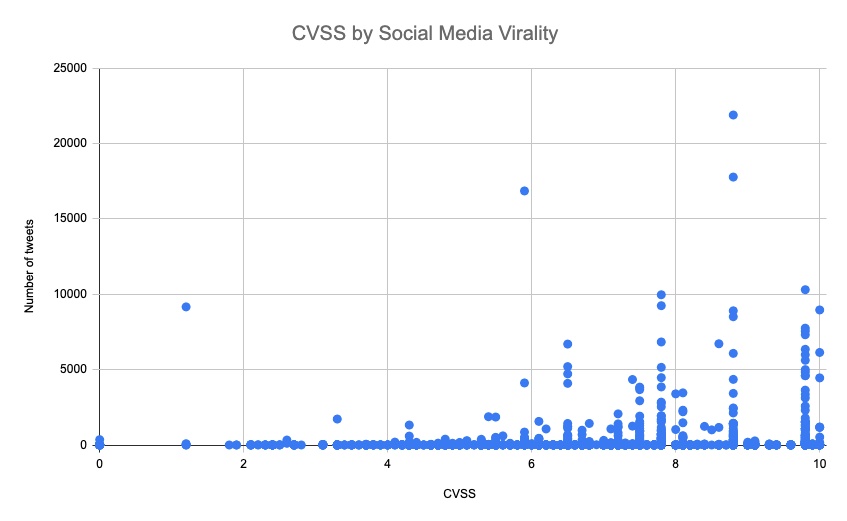
Figure 12: CVSS by Social Media Virality
Predictions for 2020
- Old faithful Injection and Cross-Site-Scripting vulnerabilities will remain at the top of the chart. Despite the awareness of these vulnerabilities and the number of tools that check code for their presence, their number won’t decrease in 2020. The reason for this is the direct impact of the exploitation of these vulnerabilities, as well as – in most cases – the lack of preconditions required to exploit them.
- The number of vulnerabilities in third-parties will continue to grow. Major platforms and frameworks rely on third-party plugins. WordPress has over 55K plugins, the NPM registry has almost 450K packages for NodeJS, and PyPI has over 210K packages for Python. In addition, there are also main package registries for Java and Ruby-based projects. As the community continues to grow, and without code standards or restrictions to publish a plugin or a package, they remain the weakest point in the application, making them the sweet spot for attackers.
- The release of the OWASP top 10 for API that standardizes the main threats in API will, on one hand, increase the awareness of security among developers. On the other hand, however, it will focus attackers and increase their attention on API vulnerabilities. Based on the previous year’s results, we expect to see constant growth, but at the same time a decrease in the growth rate.
- The security awareness among IoT vendors is still growing, so they will invest more in securing their devices. This will be reflected in the number of new vulnerabilities in IoT devices.