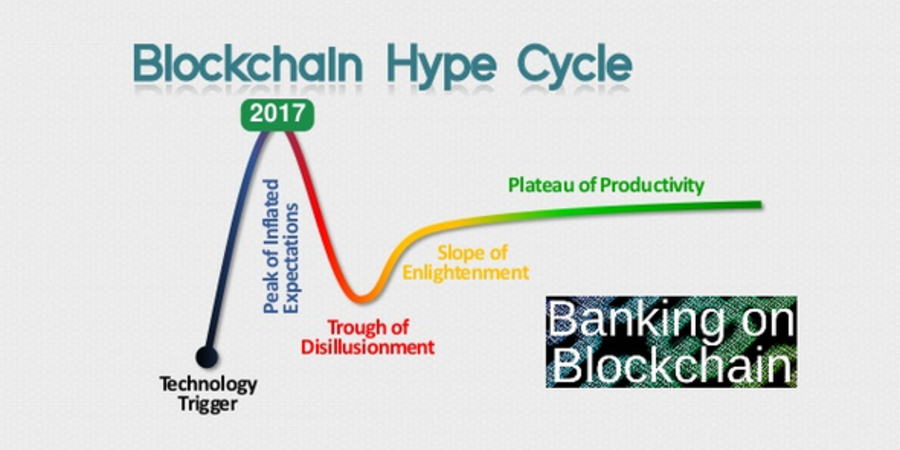
Blockchain technology alone cannot provide freshness, safety, provenance, and recall capabilities. That requires data and capabilities from outside the blockchain. It seems that the best emerging approach will be a hybrid consisting of 1) a centralized networked SaaS platform providing economical scalability and deep algorithmic and process capabilities, combined with 2) blockchain and smart contracts for transparency and validation. Blockchains are attractive because of their ability to create a shared, trusted single-version-of-the-truth between trading partners. However, a networked SaaS platform can provide a shared, trusted single-version-of-the-truth at a much lower cost.